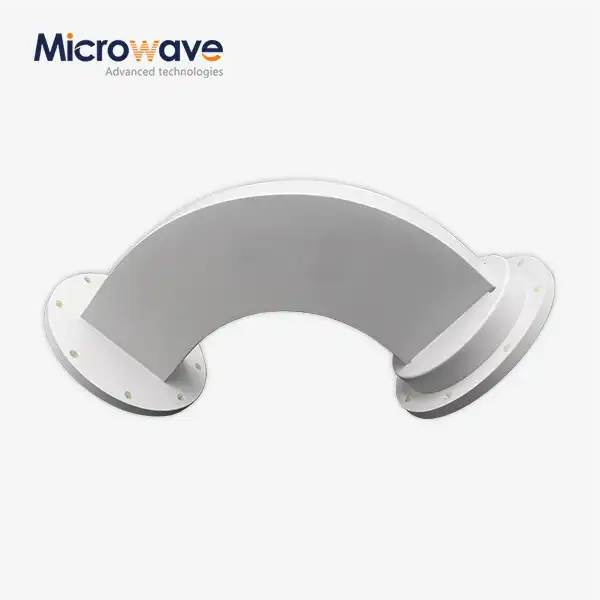
Does waveguide miter bend perform better than waveguide ARC bend?
December 3, 2024
1. Transmission Efficiency:
- Waveguide ARC bend: It has a continuous and smooth curve structure. Electromagnetic waves can travel along the curved path more smoothly during propagation, reducing reflection and scattering due to sudden direction changes. When transmitting high-frequency microwave signals, lower reflection means less energy loss, and signals can be transmitted more efficiently. In high-precision radar systems, it can maximize signal integrity and accuracy, reducing attenuation and distortion.
- Waveguide miter bend: The discontinuity at the corners easily causes reflections of electromagnetic waves. These reflected waves lead to energy loss and interfere with the main transmission waves, forming a complex electromagnetic field distribution that further affects transmission performance. In the high-frequency band, the signal wavelength is short, and the reflection effect at the corner is more obvious, potentially causing signal interruption or serious distortion.
2. Processing and Manufacturing:
- Waveguide miter bend: Its shape is relatively simple, mainly consisting of straight segments and corners of a specific angle. It can be manufactured through conventional mechanical processing methods like cutting and milling, and it's easier to control dimensional accuracy during processing. In large-scale production of some civilian microwave communication equipment with strict cost control, it can significantly reduce production costs and improve market competitiveness while meeting basic performance requirements.
- Waveguide ARC bend: The smooth curve processing is more difficult. It requires high-precision processing equipment and complex processing technology, such as CNC processing technology or special processing methods to ensure the accuracy and surface finish of the curve. This increases manufacturing cost, and the scrap rate during processing is relatively high, posing challenges in large-scale production and cost control.
3. Bandwidth Adaptability:
- Waveguide ARC bend: It can maintain relatively stable transmission performance in a wide frequency range due to its good transmission characteristics. It can adapt to the transmission of microwave signals of various frequencies and has good application prospects in broadband communication and multi-band microwave systems.
- Waveguide miter bend: Due to the reflection problem at the corners, its transmission performance at different frequencies fluctuates greatly, and its effective bandwidth is relatively narrow, which may not meet the needs of some complex communication systems with high bandwidth requirements.
In conclusion, both the angled waveguide and the curved waveguide have their advantages and limitations. The curved waveguide performs well in transmission efficiency and bandwidth adaptability, suitable for professional microwave technology fields. The angled waveguide has more advantages in processing and manufacturing, better for some civil microwave application scenarios. In practical applications, multiple factors like specific engineering requirements, cost budget, and performance indicators need to be considered comprehensively to select the appropriate waveguide bending form.
Corporate News
Can the Wideband Double-ridged Horn Antenna be customized according to different application scenarios?
What are the main working principles of Coaxial Variable Attenuators?
How to Ensure the Long-Term Stable Operation of High Power Waveguide to Coaxial Adapter?
What is the typical insertion loss and isolation for Waveguide Electromechanical Switch?
Related Blogs